ENFERMEDAD DE HODGKIN. ACTUALIZACIÓN
Dr. Horacio Oliva
1. Alvaro
Naranjo T, Salvado Usach MT, Bosch Princep R, Martinez
Gonzalez S. [p53 in Hodgkin's disease (letter)]. Med Clin
(Barc) 1996;106:398-9.
2.
Ashton-Key M, Thorpe PA, Allen JP, Isaacson PG. Follicular
Hodgkin's disease. Am J Surg Pathol 1995;19:1294-9.
3.
Cabanillas F, Pathak S, Trujillo J, Grant G, Cork A,
Hagemeister FB, Velasquez WS, McLaughlin P, Redman J, Katz R.
Cytogenetic features of Hodgkin's disease suggest possible
origin from a lymphocyte. Blood 1988;71:1615-7.
4. d'Amore ES,
Lee CK, Aeppli DM, Levitt SH, Frizzera G. Lack of prognostic
value of histopathologic parameters in Hodgkin's disease,
nodular sclerosis type. A study of 123 patients with limited
stage disease who had undergone laparotomy and were treated
with radiation therapy. Arch Pathol Lab Med 1992;116:856-61.
5. Doggett RS,
Colby TV, Dorfman RF. Interfollicular Hodgkin's disease. Am J
Surg Pathol 1983;7:145-9.
6. Martinez JC, Piris MA,
Sanchez-Beato M, Villuendas R, Orradre JL, Algara P,
Sanchez-Verde L, Martinez P. Retinoblastoma (Rb) gene product
expression in lymphomas. Correlation with Ki67 growth
fraction. J Pathol 1993;169:405-12.
7. Morente MM,
Piris MA, Abraira V, Acevedo A, Aguilera B, Bellas C, Fraga
M, Garcia-Del-Moral R, Gomez-Marcos F, Menarguez J, et al.
Adverse clinical outcome in Hodgkin's disease is associated
with loss of retinoblastoma protein expression, high Ki67
proliferation index, and absence of Epstein-Barr virus-latent
membrane protein 1 expression [In Process Citation]. Blood
1997;90:2429-36.
8.
Orschesche K, Merz H, Hell J, Feller AC. Presence of the
t(2;5) in Hodgkin's disease [letter; comment]. Blood
1995;86:4383-5.
9.
Sanchez-Beato M, Martinez-Montero JC, Doussis-Anagnostopoulou
TA, Gatter KC, Garcia J, Garcia JF, LLoret E, Piris MA.
Anomalous retinoblastoma protein expression in Sternberg-Reed
cells in Hodgkin's disease: a comparative study with p53 and
Ki67 expression. Br J Cancer 1996;74:1056-62.
10. Tilly H,
Bastard C, Delastre T, Duval C, Bizet M, Lenormand B, Dauce
JP, Monconduit M, Piguet H. Cytogenetic studies in untreated
Hodgkin's disease. Blood 1991;77:1298-304.
11. Yee HT, Ponzoni M,
Merson A, Goldstein M, Scarpa A, Chilosi M, Menestrina F,
Pittaluga S, de Wolf-Peeters C, Shiota M, et al. Molecular
characterization of the t(2;5) (p23; q35) translocation in
anaplastic large cell lymphoma (Ki-1) and Hodgkin's disease.
Blood 1996;87:1081-8.
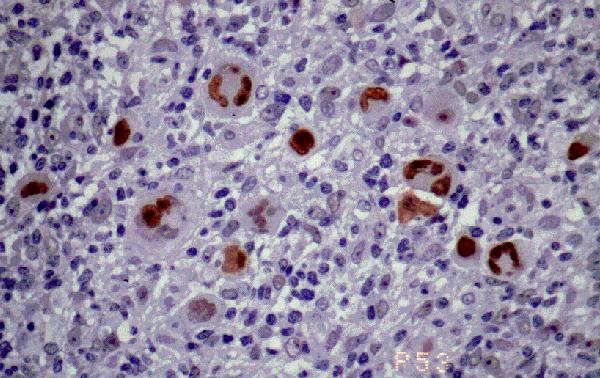 |
Figura 18. p53 en enfermedad
de Hodgkin. Sólo las células grandes atípicas,
de Hodgkin y R-S
muestran inmunotinción, no existiendo elementos
linfoides de pequeño o mediano tamaño
positivos.
Cerca del 100% de los casos de enfermedad de
Hodgkin son positivos. P53. En la foto se
observan células de Reed-Sternberg positivas
para p53. |
[ÍNDICE]
[INTRODUCCIÓN]
[ESTUDIO
INMUNOHISTOQUÍMICO Y CITOGENETICO] [TIPOS Y SUBTIPOS DE LA EH]
